Types of Gum Diseases
1. Gingivitis (Gum Inflammation)
At its early stage, bacteria in plaque build-up, causing the gums to become inflamed and to easily bleed during tooth brushing.
Although the gums may be irritated, the teeth are still firmly planted in their sockets. No irreversible bone or other tissue damage has occurred at this stage.
Without proper treatment, this may progress into periodontitis.
2. Periodontitis
In a person with periodontitis, the inner layer of the gum and bone pull away from the teeth and form pockets as a result of further gum inflammation.
As the disease progresses, the pockets deepen and more gum tissue and bone are destroyed.
When this happens, your teeth become loose and eventually drops off.
As such, periodontitis is the leading cause of tooth loss in adults.
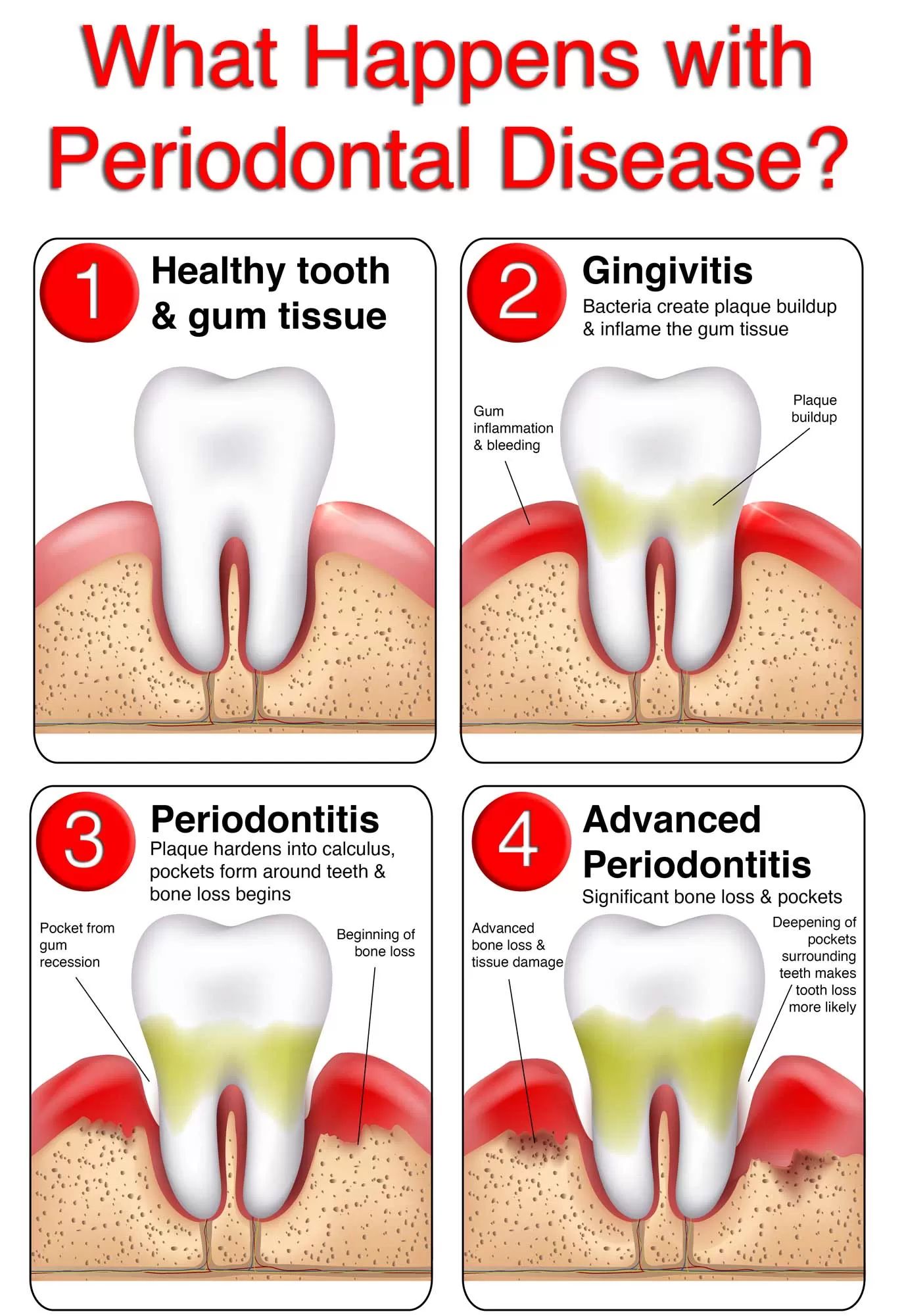
What are the Risk Factors that Contribute to Gum Disease?
Plaque, which is a form of bacterial build-up on teeth, is the primary cause of gum disease. However, other factors can contribute to periodontal problems. These include:
- Hormonal changes, such as those occurring during pregnancy, puberty, menopause, and monthly menstruation, make gums more sensitive, which makes it easier for gingivitis to develop.
- Illnesses may affect the condition of your gums. This includes diseases such as cancer or HIV that interfere with the immune system.
- Because diabetes affects the body's ability to use blood sugar, patients with this disease are at higher risk of developing infections, including periodontal disease and cavities.
- Medications can affect oral health because some lessen the flow of saliva, which has a protective effect on teeth and gums.
- Some drugs, such as the anticonvulsant medication Dilantin and the anti-angina drug Procardia and Adalat, can cause abnormal growth of gum tissue.
- Bad habits such as smoking make it harder for gum tissue to repair itself.
- Poor oral hygiene habits such as not brushing and flossing daily
- Family history of dental disease can contribute to the development of periodontal issues
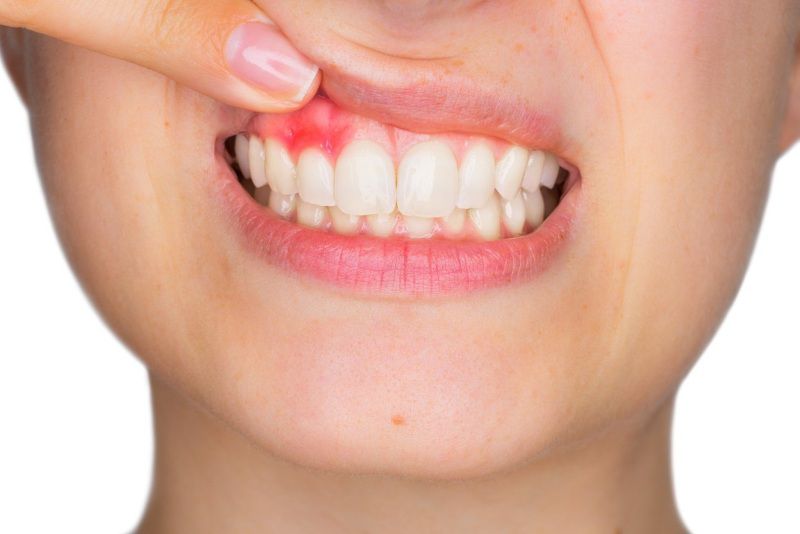
What Are the Symptoms of Gum Disease?
Gum disease may progress painlessly, producing few obvious signs, even in the late stages of the disease. Although the symptoms of periodontal disease often are subtle, the condition is not entirely without warning signs. Certain symptoms may point to some form of the disease. The symptoms of gum disease include:
- Gum Infection
- Gums that bleed during and after tooth brushing
- Red, swollen gums. Healthy gums should be pink and firm.
- Persistent bad breath or bad taste in the mouth
- Receding gums
- Formation of deep pockets between teeth and gums
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Changes in the way teeth fit together upon biting down, or in the fit of partial dentures
Even if you don't notice any symptoms, you may still have some degree of gum disease. In some people, gum disease may affect only certain teeth, such as the molars. Only a dentist or a periodontist can recognize and determine the progression of gum disease.
FAQs
Allsmiles Dental Care offers gum treatment at the following prices:
Regular scaling and polishing:
$70 to $120
Stain removal:
$35 to $50
Deep cleaning:
Per tooth $50 onwards
Per quadrant $100 to $250
These are some of the things you can do for prevention:
- Brush your teeth twice a day
- Floss at least once a day
- Visit your dentist for regular maintenance
- If you have diabetes, ensure that it is well controlled
- Quit smoking
No. Stain removal and polishing only remove superficial stains such as those from coffee, tea and smoking.
Tooth whitening, on the other hand, changes the intrinsic color of your teeth.